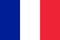
Hip joint arthrosis (deforming arthrosis, coxarthrosis, osteoarthrosis) is a progressive degenerative-dystrophic disease, which leads to time to destroy affected, persistent and limiting mobility.
The disease affects people over the age of 40, women are sick several times more often than men.
In the overall structure of arthrosis, the arthrosis of the hip joint belongs to the main role.This is due to the widespread congenital pathology of the hip joints (displacements), as well as significant physical energy, which are vulnerable to.
Risk factors and causes of hip joint arthrosis
In the pathological mechanism of the development of hip joint arthrosis, the main role belongs to the changes in the physicochemical properties of synovial fluid (intra-articular), as a result it becomes more compact and viscous.This exacerbates the quality of the lubricant.When moving, the surface of the cartilage together begins to rub each other, becoming rough, covered with cracks.Small particles of Hyalin cartilage are left and fall into the articular cavity, causing the development of aseptic (non -shiny) inflammation in it.When the disease occurs into the process of inflammation, the bone tissue is drawn to the inflammation process, leading to aseptic necrosis of the femoral head and the acetabulum surface, the formation of osteophytes (bone growth), increases inflammation and causes severe pain during movement.
In the final stage of the arthrosis of the hip joint, inflammation is also thrown into the joints around the tissue (blood vessels, nerves, ligaments, muscles), leading to the appearance of periarthritis signs.As a result, the hip joint is completely destroyed, its function is gone, the movement in it stops.This condition is called ankylosis.
Causes of arthrosis of the hip joint:
- Congenital lips of the thighs;
- hip displacement;
- femoral aseptic necrosis;
- Peters disease;
- hip joint injury;
- infectious arthritis of the hip joint;
- gonarthrosis (deformation of osteoarthrosis of the knee joint);
- osteochondrosis;
- Overweight;
- professional sports;
- flat feet;
- spinal curvature;
- An inactive lifestyle.
Pathology is not inherited, but children inherit the characteristics of the musculoskeletal system structure from their parents, which can cause hip joint arthrosis in this condition.This describes the facts of the family existence, a higher event than the general population.
A form of a disease
Depending on the etiology, the arthrosis of the hip joint is divided into primary and secondary.Secondary arthrosis develops with a background of other diseases from the hip joint or injury.The main forms are not related to previous pathologies, as their development is often impossible, in this case they are talking about idiopathic arthrosis.
Coksartrosis is one or bilateral.
Phase
Three levels (degrees) are distinguished during hip joint arthrosis:
- Early pathological changes - are stated slightly, provided timely and adequate treatment can be reversed.
- Progressive coxarthrosis - characterized by a gradual increase in symptoms (joint pain and damage to its movement), changes in the joint tissue are irreversible, but therapy can slow down the degenerative process.
- The final movement of the joints is gone, ankylosis is formed.Treatment is only possible surgery (replacing joints with artificial).
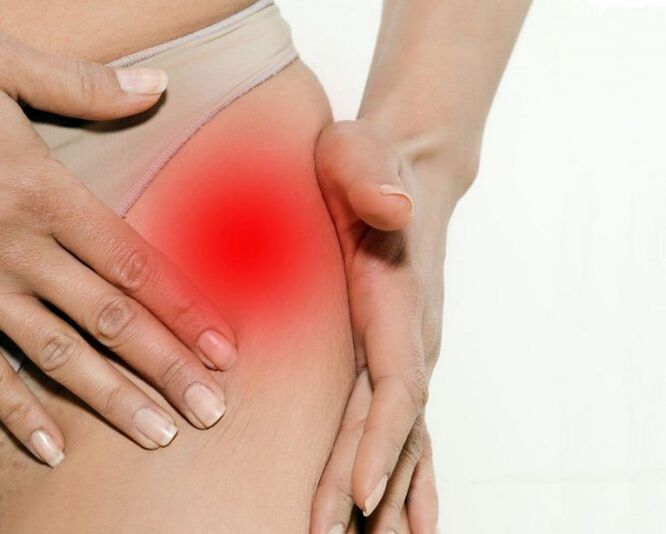
Endoprosthetics surgery in 95% of cases ensures complete mobility recovery of the limbs, restoring the patient's performance.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the hip joint
The main signs of hip joint arthrosis:
- pain in the thighs, hips and knees;
- the feeling of stiffness in the affected joints and the limitations of its mobility;
- Disadvantages;
- abduction restrictions;
- Atopic changes in the thigh muscles.
The presence of certain symptoms of hip joint arthrosis, as well as their severity depends on the level of the disease.
In the first stage of hip joint arthrosis, the patient complains of pain in the affected joints that occur under the influence of physical activity (walking, walking).In some cases, the pain is localized in the knee or thigh area.After a short break, the pain passed by itself.The amount of movement of the limbs is fully maintained, running not damaged.The following changes are recorded on radiography:
- little uneven decline in the lumen of the joint gap;
- Osteophytes are located on the interior edge of rotation.
Any changes from the neck and femoral heads are not detected.
With the level of arthrosis of the hip joint, pain also occurs at rest, including at night.After physical activity, the patient begins to drown, the "duck" characteristic features are formed.So -Called Stoult Pain appears - after a long period of immobility, the first few steps cause pain and discomfort, which then pass and then return after a long load.In the affected joints, the amount of movement (abduction, internal rotation) is limited.Radiographs indicate that the joint gap is uneven and the lumen is 50% of the norm.Osteophytes are located along the internal and external edges of the joint cavity, over the cartilage boundaries.The contour of the femoral head becomes uneven due to deformation.
With the level of arthrosis III of the hip joint pain, intense and persistent, does not stop at night.Walking is very difficult, the patient has to rely on sugarcane.The amount of movement in the affected joints is limited, then it stops completely.Due to the hip muscle atrophy, the pelvis deviates in the frontal plane and the limbs are shortened.Trying to balance this shortening, patients during walking are forced to push the body towards the lesion, which in turn increases the burden on the joints.In radiography, various bone growth, significant narrowing of the joint gap and significant increase in the femur head is detected.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of hip joint arthrosis is based on the clinical picture of the disease, medical examination results and instrumental studies, including the main value of visualization - radiography, resonance or magnetic calculation.They allow not only to determine the presence of arthrosis of the hip joint and evaluate his degree, but also to identify possible causes of disease (trauma, young epiphysiolysis, Peters disease).
Diagnosis of differential arthrosis of the hip joint with other diseases of the musculoskeletal system is quite complicated.At the levels of arthrosis II and III hip joints, muscle atrophy develops, which can cause intensive pain in the driving joint characteristics or gonarthrosis (knee joint disease).For the diagnosis of these different states, the knee palpation and hip joints feel, the amount of movement in it is determined, and they are also radiologically examined.
In spinal diseases, in some cases, the nerve root of the spinal cord with the development of the pain syndrome is squeezed.Pain can emit the hip joint area and mimic the clinical picture of its defeat.However, the nature of the pain with radicular syndrome is slightly different from the arthrosis of the hip joint:
- Pain occurs due to weight loss or sharp movement, and is not under the influence of physical meaning;
- The pain is localized in the gluteal, not the inguinal region.
With radicular syndrome, the patient can calmly take his feet to the side, while with the arthrosis of the hip joint, the abduction is limited.The characteristic signs of radicular syndrome are positive symptoms of tension - the appearance of sharp pain while trying to raise the foot straight behind the patient.
Hip joint arthrosis affects people over 40, women are sick several times more often than men.
Hip joint arthrosis should also be distinguished by trochanteritis.Vable bursitis develops faster, within a few weeks.He is usually preceded by significant physical injury or injury.In this disease, the pain is more significant than with the arthrosis of the hip joint.At the same time, shortening the limbs and limiting the mobility is not detected.
Clinical picture of atypical reactive arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis can resemble clinical manifestations of hip joint arthrosis.However, pain occurs in patients especially at night or rest, while walking is not intensive, but, on the contrary, weakens.In the morning, the patient recorded stiffness in the joints, which passed after a few hours.
Treatment of hip joint arthrosis
Orthopedia is involved in the treatment of hip joint arthrosis.With the stages of I and II disease, conservative therapy is indicated.With the so -called pain syndrome, the patient is prescribed anti -inflammatory drugs that are not prescribed in short courses.They are unacceptable for a long time, as they can not only negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract, but also suppress the hyalin cartilage regenerative ability.
In the hip joint arthrosis treatment regimen, they include chondroprotectors and vasodilators, which create optimal opportunities to recover damaged cartilage tissue.With spoken muscle spasms, it may require the appointment of central muscle relaxants.
In these cases when it is not possible to stop the pain syndrome with anti -anti -Ssteroid drugs, using intraarticular injection of corticosteroids.
Local treatment of hip joint arthrosis using heating ointment allows you to reduce muscle cramps and slightly weaken pain due to disturbing actions.
In complex therapy of hip joint arthrosis, physiotherapy methods are also used:
- magnetotherapy;
- inductothermia;
- Uhf;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound treatment;
- Massage;
- medical gymnastics;
- Manual therapy.
Nutrition for hip joint arthrosis is intended to correct weight and normalization of metabolic processes.Losing weight reduces the burden on the hip joint and thus slows down the development of the disease.
To unload the affected joints, the doctor may recommend that the patient go to the stick or sugarcane.
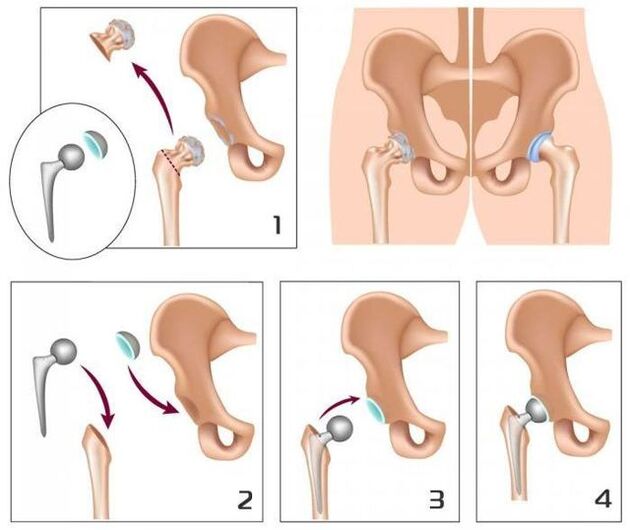
With the level of arthrosis III hip joint, conservative treatment is inefficient.In this case, it is possible to improve the condition of the patient, it is possible to restore normal mobility only due to surgical intervention - to replace the destroyed joints (joint endoprostetics).
Possible consequences and complications
The most serious complication of the progressive arthrosis of the hip joint is a defect due to loss of movement in the joint.With bilateral coksartrosis, the patient loses his ability to move independently and requires persistent external care.Living in bed in one position creates a prerequisite for the occurrence of inflammation of the lungs (hypostatic), which is difficult to lower and can cause death.
Pathology is not inherited, but children inherit the characteristics of the musculoskeletal system structure from their parents, which can cause hip joint arthrosis.
Prophesy
Hip joint arthrosis is a progressive chronic disease, which can be completely cured in the early stages, subject to the elimination of the cause of the disease.In other cases, therapy allows you to slow down its journey, however, over time, there is a need for hip endoprostheses implantation.Such surgery in 95% of cases provides a complete recovery of limbs, restoring the patient's performance.The life of modern prosthesis service is 15-20 years, after which they are subject to replacement.
Prevention
Prevention of hip joint arthrosis aims to eliminate the causes that can lead to the development of the disease, and include:
- timely detection and treatment of diseases and hip joint injuries;
- rejection of inactive, normal, but not excessive physical activity;
- weight control;
- rational nutrition;
- Rejection of bad habits.